Bootstrap Columns Form
Intro
In the previous several years and certainly the upcoming ones to come the universe of internet spreading more and a lot more largely throughout each variety of gadgets so now practically fifty percent of the views of the pages out there are carried out not really on desktop and laptop computer displays but from numerous mobile products along with every kinds of small-scale display screen dimensions. In this way supposing that a webpage will not show properly-- suggesting to resize and quickly find its best match on the device utilized its most likely will get searched away to become removed and replaced by a mobile phone friendly web page providing identical service or product.
In addition-- the indexing engines like Google operate the so called mobile-friendly test and reveal far down your pages inside of the search results. This pushing down is even farther assuming that the search is executed by a mobile device-- the internet search engines look upon this particular subject quite seriously. In this way not providing a mobile phone friendly webpage almost signifies not having a web page in any way.
The best ways to use the Bootstrap Columns jQuery:
Although just what actually a page becoming responsive means-- usually-- fitting all width of the screen which gets showcased on providing the elements in useful and clear way at any sizing. To care for this the Bootstrap framework uses so called breakpoints and columns . In a few words the breakpoints are predefined display widths at which a shift happens and the Bootstrap Columns Form become reordered to hopefully fit in preferable. The prior version utilized 4 breakpoints and one of the most recent Bootstrap 4 system launches one added so they get in fact five. Here they are along with the highest value they stretch to. The precise boundary number in itself refers to the next display scale.
Extra small up to 34em ( or 544px) – up to Bootstrap 4 Alpha 5 had the -xs- infix. In Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 this infix is dropped so just the number follows;
Small – from 34em up to 48em ( or 768px ) – has the -sm- infix;
Medium – from 48em up to 62em ( or 992px ) – has the -md- infix;
Large – from 62em up to 75em ( 1200px ) - -lg- infix;
Extra large – 75em and everything above it – the new size in Bootstrap 4 – has the -xl- infix.
More techniques
The horizontal sector in Bootstrap 4 system becomes divided into 12 parts equivalent in width-- these are the so called columns-- they all carry the .col- prefix. Next goes the screen dimension infix which specified down to which display size the column component will span the specified amount of columns. Supposing that the screen scale is more compact -- the column feature possesses the full display screen width-- like it was specified .col-12 (.col-xs-12 up to Bootstrap 4 alpha 5).
Auto style columns
Employ breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Incorporate any quantity of unit-less classes for every breakpoint you require and each and every Bootstrap Columns Stack will definitely be the equal width.
Equal size
For instance, below are two grid styles that placed on every device and viewport, from xs.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Putting one column size
Auto-layout for flexbox grid columns likewise indicates you are able to put the width of one column and the others will instantly resize all around it. You may utilize predefined grid classes ( just as demonstrated here), grid mixins, as well as inline widths. Note that the other columns will resize despite the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable size content
Utilizing the col- breakpoint -auto classes, columns are able to size itself founded on the common width of its content. This is extremely practical along with single line content just like inputs, numbers, etc. This, along with horizontal alignment classes, is incredibly valuable for focusing formats with uneven column sizes as viewport width improves.
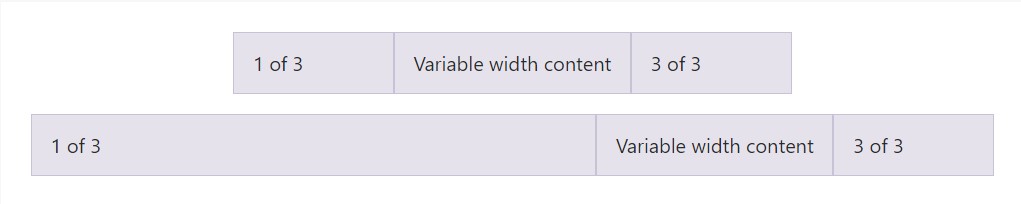
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Equivalent size multi-row
Establish equal-width columns which go across multiple rows via filling in a .w-100 precisely where you want the columns to break to a new line. Develop the breaks responsive simply by mixing the .w-100 together with some responsive display utilities.
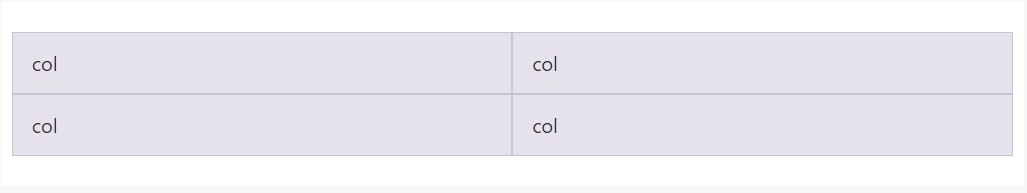
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>One more new thing
Another new thing among the most recent Alpha 6 build of Bootstrap 4 is in the event that you add simply just a handful of .col-~ some number here ~ elements spanning less than 12 columns they will really distribute proportionally to get all the zone accessible on the row and will continue being this way at any display width-- and even under 32em.
Conclusions
And so now you recognize precisely how the column components set up the design as well as responsive behavior of the Bootstrap system and all that is really left for you is setting up something truly wonderful using them.
Take a look at several online video tutorials relating to Bootstrap columns
Connected topics:
Bootstrap columns main information

Responsive columns in Bootstrap
Problem with a heights of the Bootstrap columns